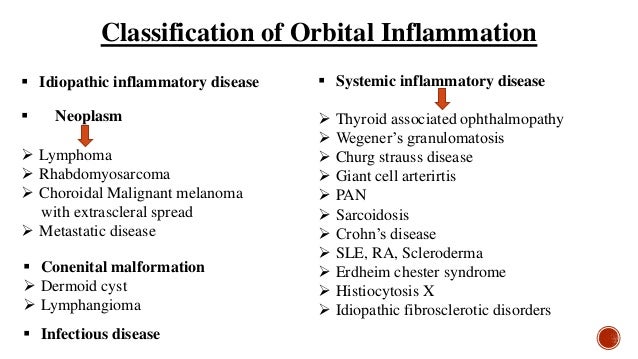
Idiopathic Orbital Inflammatory Disease
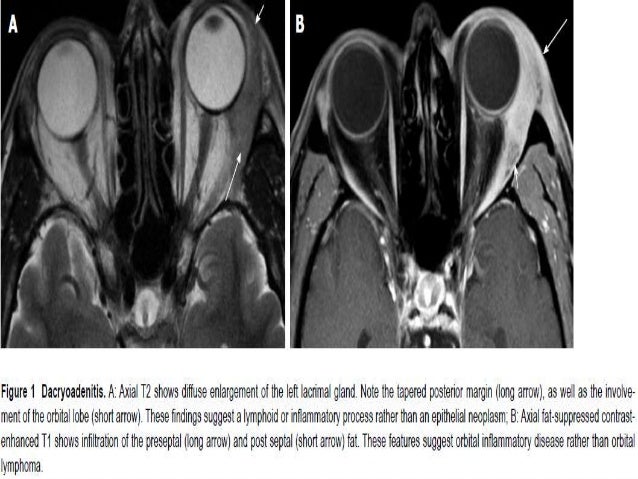
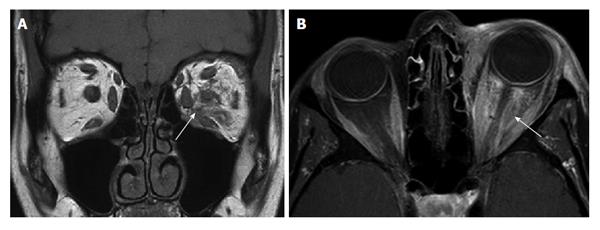
Idiopathic orbital inflammatory disease. NSOI can be localized or diffuse. It most commonly affects patients in the third decade of life with a female predilection 1. Dacryoadenitis of lacrimal glands myositis of extraocular muscles perineuritis of optic nerve orbital ce.
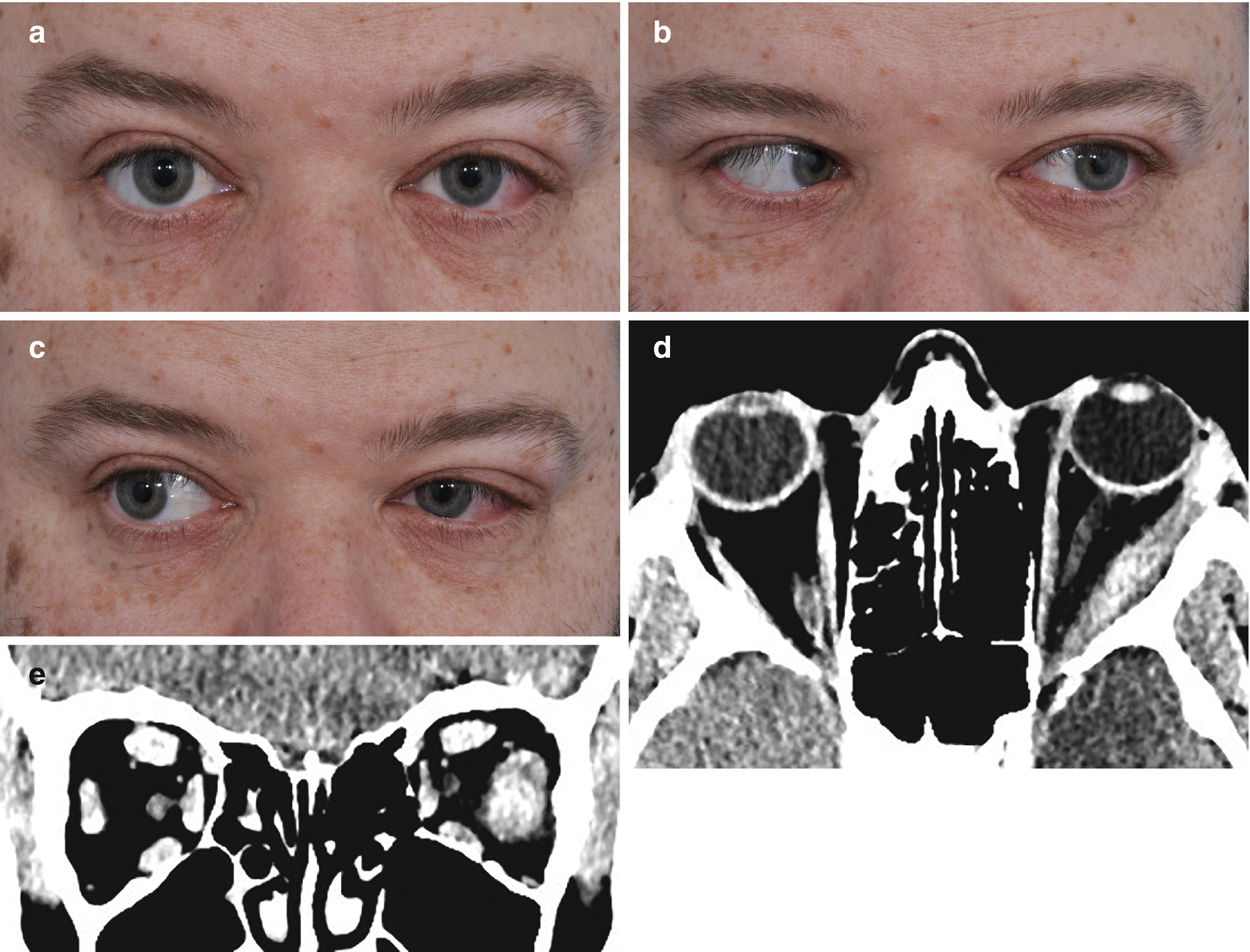
Idiopathic orbital inflammation is a multifaceted disease with a wide spectrum of clinical radiological and histopathological presentations. Ophthalmic disease occurs in 25 to 50 of patients with sarcoidosis among which Anterior and posterior uveitis are common. Patients with sub-acute or chronic idiopathic orbital inflammation more than 14 days.
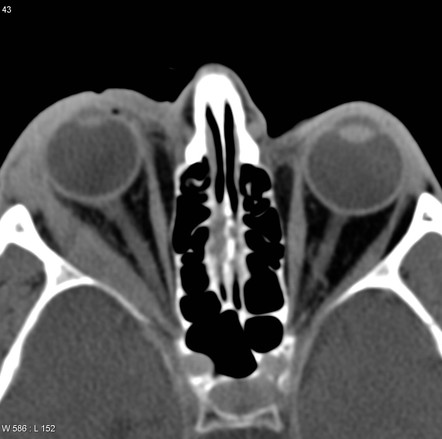
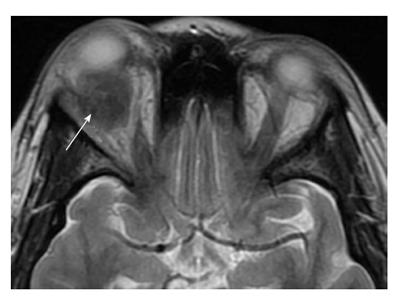
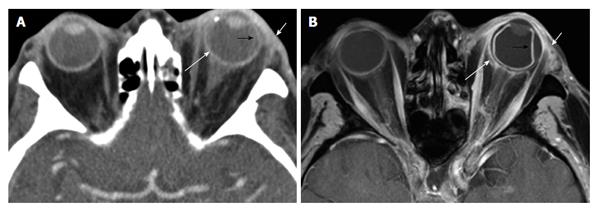
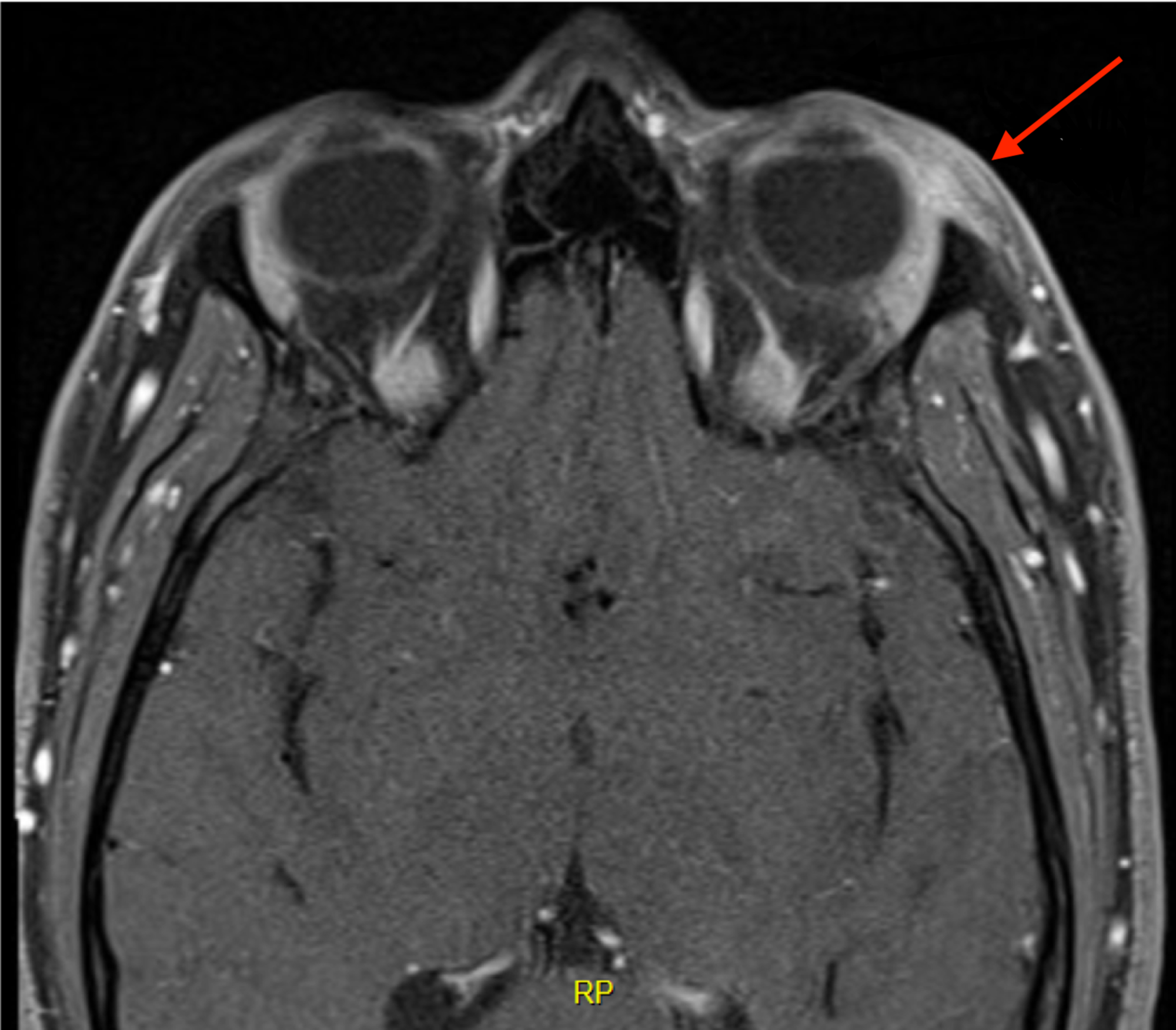
The purpose of this study was to review our clinical experience with 132 idiopathic orbital inflammation cases seen between 1971 and 1994. 38 Contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging MRI is. An insidious onset may arise from a more chronic progressive disease such as idiopathic sclerosing orbital inflammation.
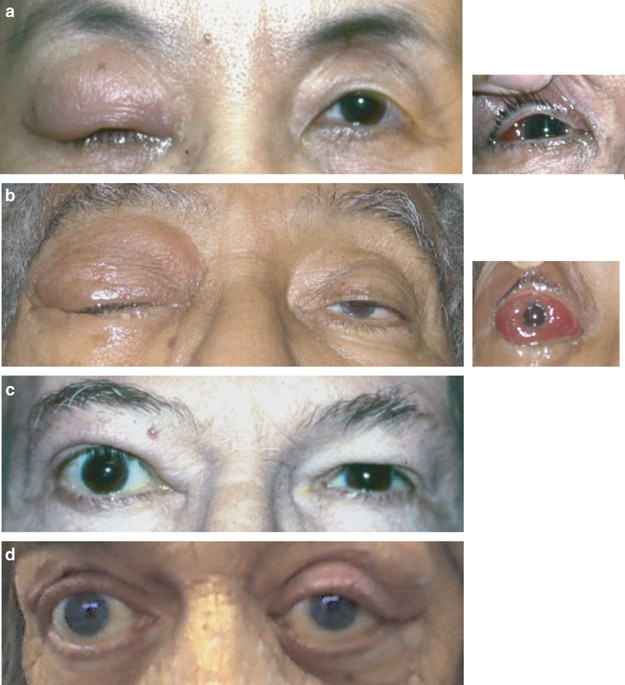
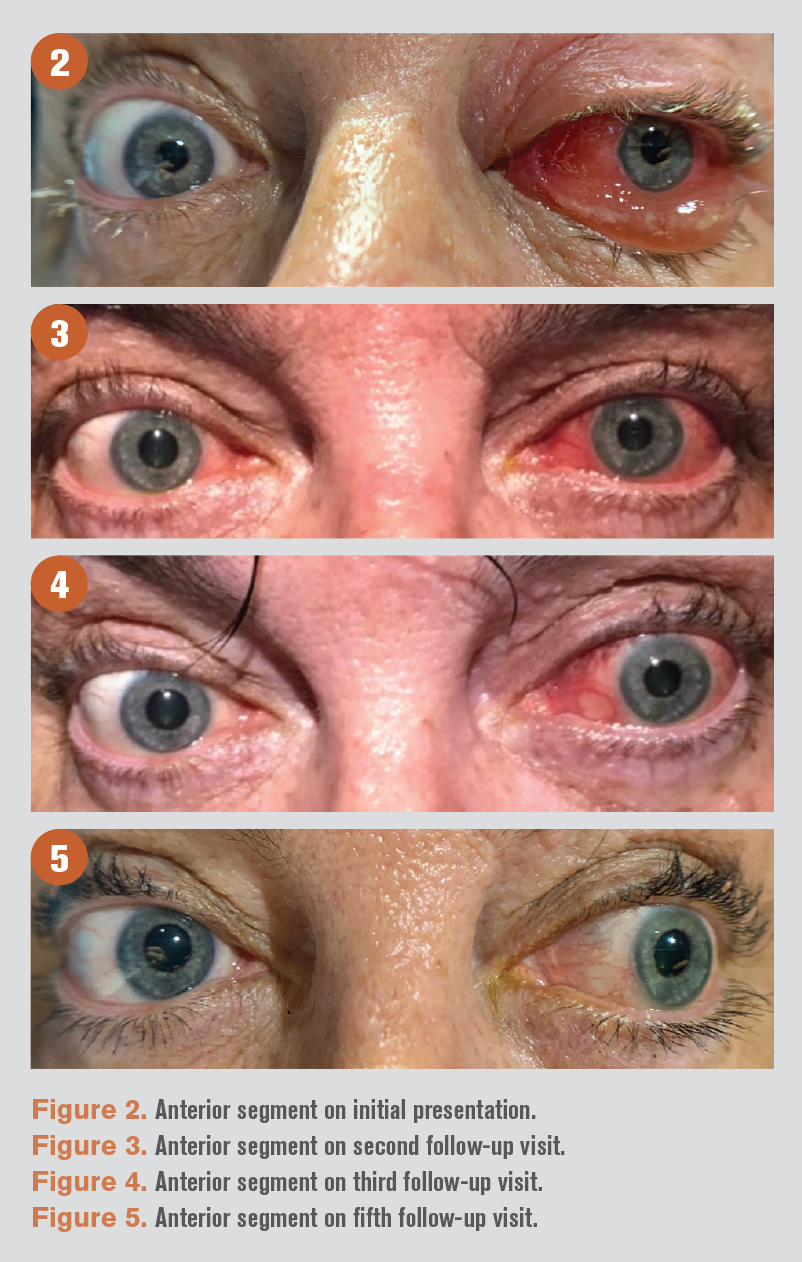
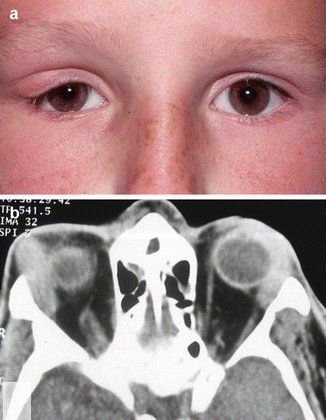
Clinical charts of the patients were evaluated retrospectively. In four pediatric patients isolated orbital pseudotumor preceded the development of a systemic inflammatory disease including pauciarticular juvenile idiopathic arthritis eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis Churg-Strauss syndrome granulomatosis with polyangiitis Wegeners granulomatosis and Crohns disease. Sarcoid infiltration of the orbit is less common which is present in approximately 14th of cases with ocular involvement and up to 10 of all patients.
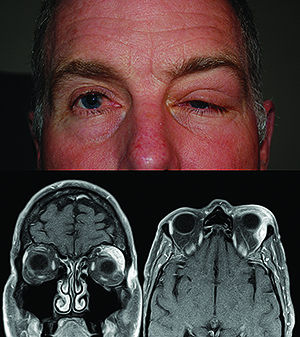
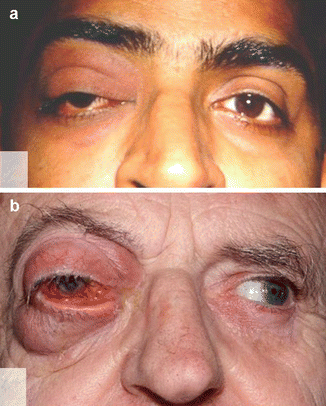
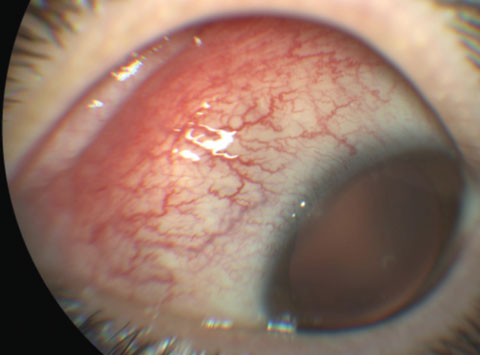
Up to 10 cash back Idiopathic orbital inflammatory disease IOID is a group of inflammations without a known systemic or local cause the principal diseases to be excluded being atypical thyroid eye disease sarcoidosis collagen vascular diseases such as ANCA-associated vasculitis IgG4-related sclerosing inflammatory disease or systemic lupus erythematosus or various. Nonspecific orbital inflammation NSOI also known as orbital inflammatory pseudotumor idiopathic orbital inflammation IOIand orbital inflammatory syndrome is the most common cause of painful orbital mass in adults. Idiopathic orbital inflammatory syndrome also known as orbital pseudotumor is a syndrome of non-specific inflammation of orbital tissue s with no identifiable local or systemic cause.
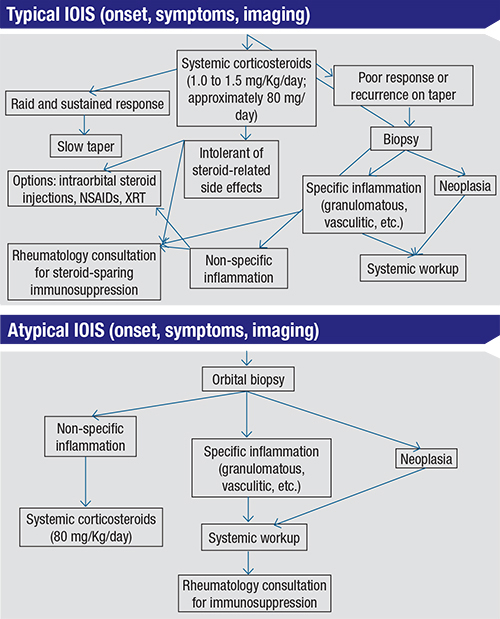
Idiopathic orbital inflammation formerly inflammatory pseudotumour is a non-granulomatous inflammatory process within the orbit for which there is no recognized local cause or any underlying systemic disease. Idiopathic orbital inflammatory syndrome IOIS also known as orbital pseudotumor is one of the most common acute orbital processes. The diagnosis of Acute Idiopathic orbital inflammation was based on the presence of symptoms and signs of acute orbital inflammation associated with the characteristic findings in the orbital imaging in the absence of any identifiable local or systemic cause.
Idiopathic orbital inflammation IOI is by definition idiopathic although sometimes it is associated with systemic disease such as inflammatory bowel disease or. IOIS can involve virtually any orbital tissue individually or in combination.
Patients with sub-acute or chronic idiopathic orbital inflammation more than 14 days.
IgG4-related systemic disease IgG4-RD is an inflammatory condition of unknown etiology that has been identified as the cause of tumefactive lesions in a number of tissues and organs. IgG4-related systemic disease IgG4-RD is an inflammatory condition of unknown etiology that has been identified as the cause of tumefactive lesions in a number of tissues and organs. IOIS can involve virtually any orbital tissue individually or in combination. Idiopathic orbital inflammatory syndrome IOIS also known as orbital pseudotumor is one of the most common acute orbital processes. Clinical charts of the patients were evaluated retrospectively. Nonspecific orbital inflammation NSOI also known as orbital inflammatory pseudotumor idiopathic orbital inflammation IOIand orbital inflammatory syndrome is the most common cause of painful orbital mass in adults. It most commonly affects patients in the third decade of life with a female predilection 1. In four pediatric patients isolated orbital pseudotumor preceded the development of a systemic inflammatory disease including pauciarticular juvenile idiopathic arthritis eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis Churg-Strauss syndrome granulomatosis with polyangiitis Wegeners granulomatosis and Crohns disease. Ophthalmic disease occurs in 25 to 50 of patients with sarcoidosis among which Anterior and posterior uveitis are common.
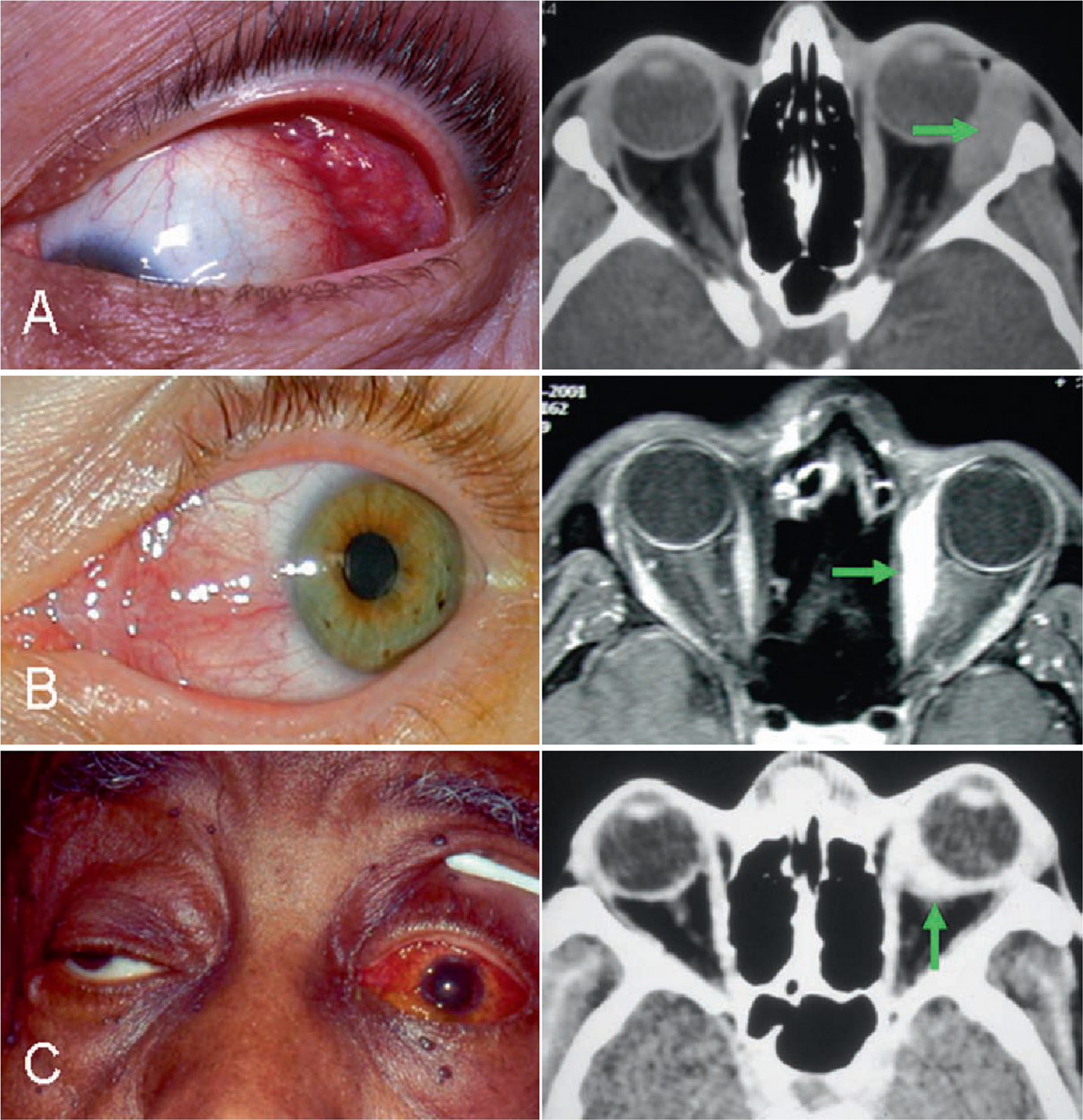
The diagnosis of Acute Idiopathic orbital inflammation was based on the presence of symptoms and signs of acute orbital inflammation associated with the characteristic findings in the orbital imaging in the absence of any identifiable local or systemic cause. IOIS can involve virtually any orbital tissue individually or in combination. 38 Contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging MRI is. Ophthalmic disease occurs in 25 to 50 of patients with sarcoidosis among which Anterior and posterior uveitis are common. Nonspecific orbital inflammation NSOI also known as orbital inflammatory pseudotumor idiopathic orbital inflammation IOIand orbital inflammatory syndrome is the most common cause of painful orbital mass in adults. Idiopathic orbital myositis IOM is a rare clinical condition characterized by idiopathic inflammation primarily involving the extraocular muscles. The differential diagnosis of orbital inflammatory diseases including orbital pseudotumors can be divided based on their location into.






















Post a Comment for "Idiopathic Orbital Inflammatory Disease"