Interstitial Lung Disease Radiology
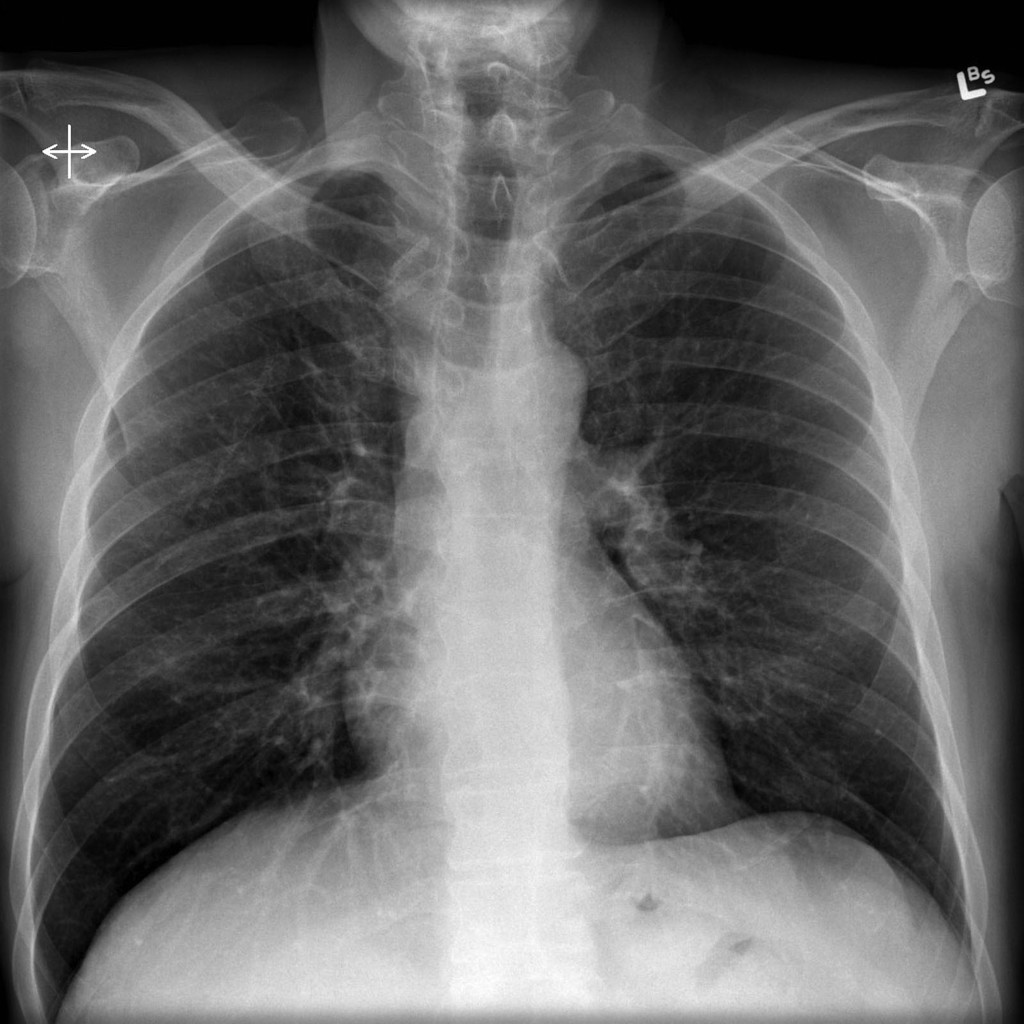
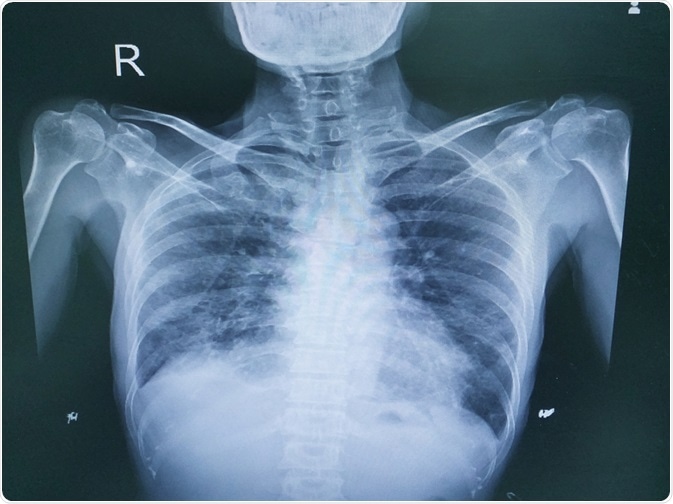
Interstitial lung disease radiology. On a Chest X-Ray it can be very difficult to determine whether there is interstitial lung disease and what kind of. Leflunomide-induced acute interstitial pneumonia. IIPs include seven entities.
Residual pulmonary disease is sometimes referred to as post-COVID interstitial lung disease ILD. In this issue of Radiology Han and Fan et al 1 report on a prospective cohort of 114 patients with severe COVID-19 pneumonia undergoing CT during hospital admission and 6 months later. Cryptogenic organizing pneumonia COP.
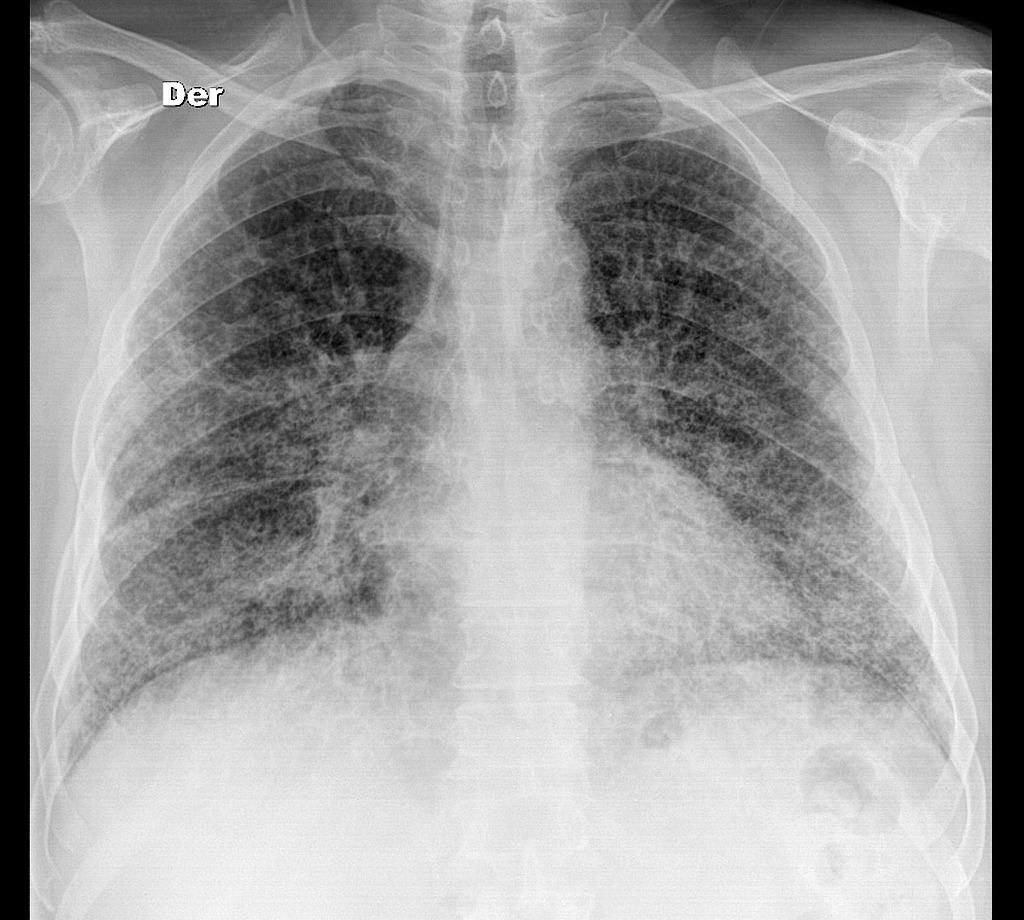
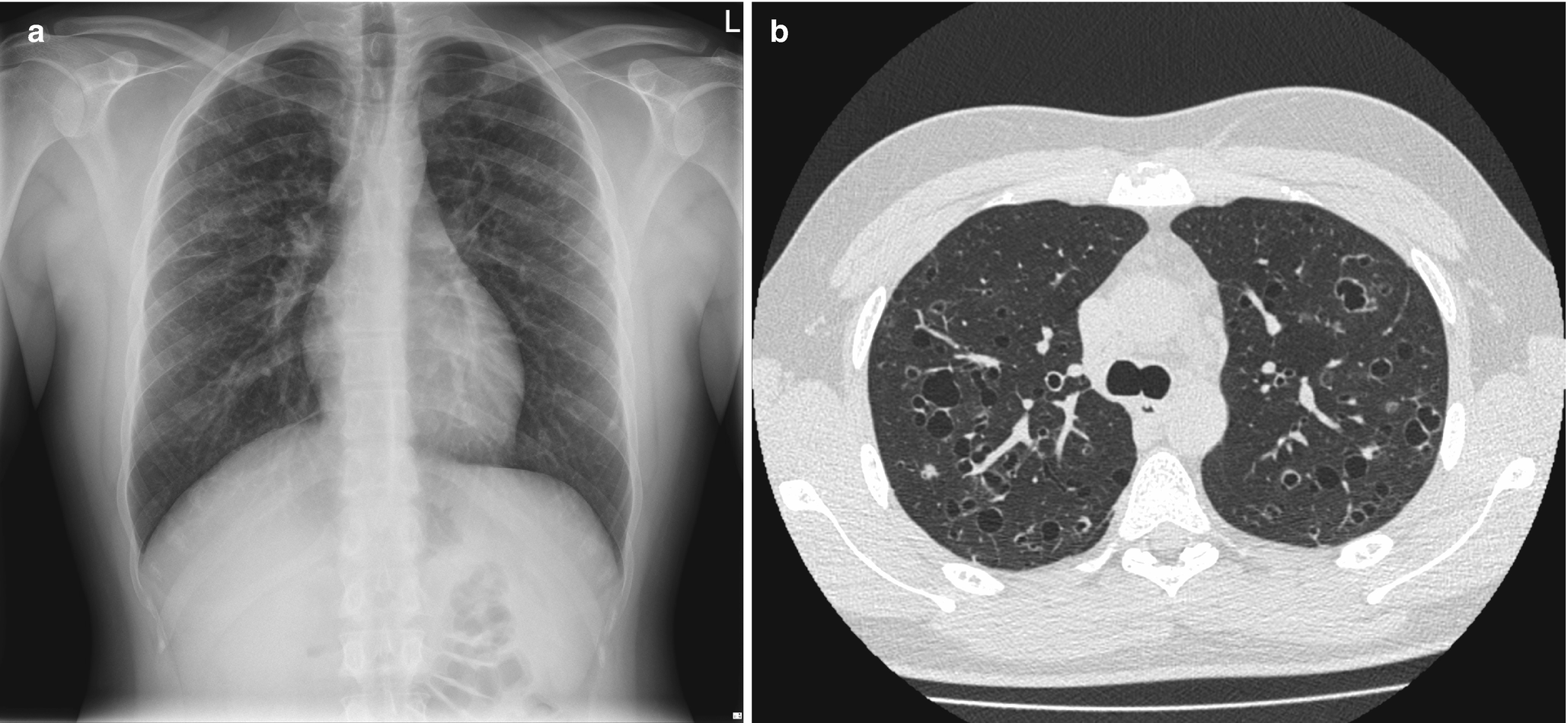
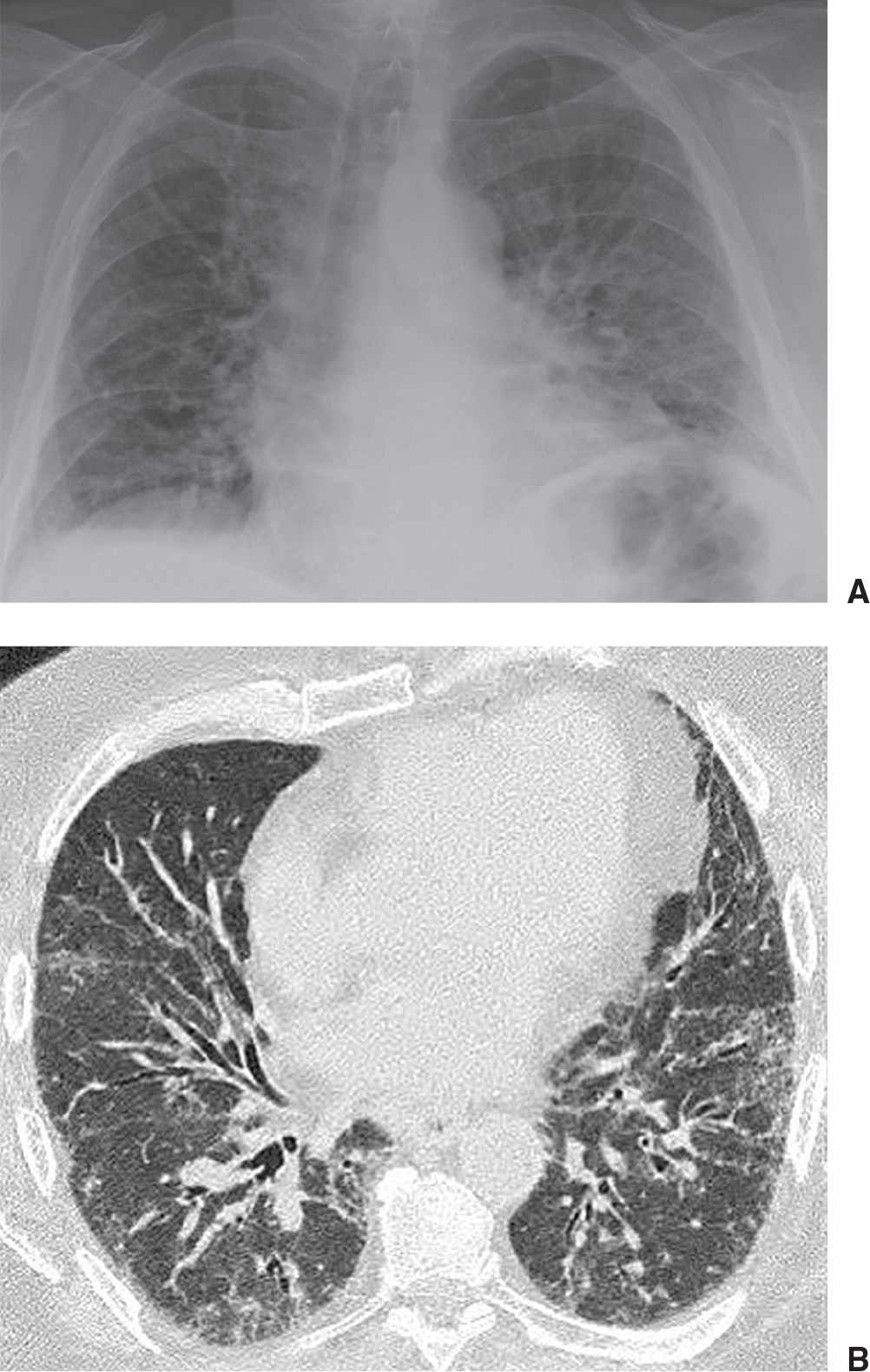
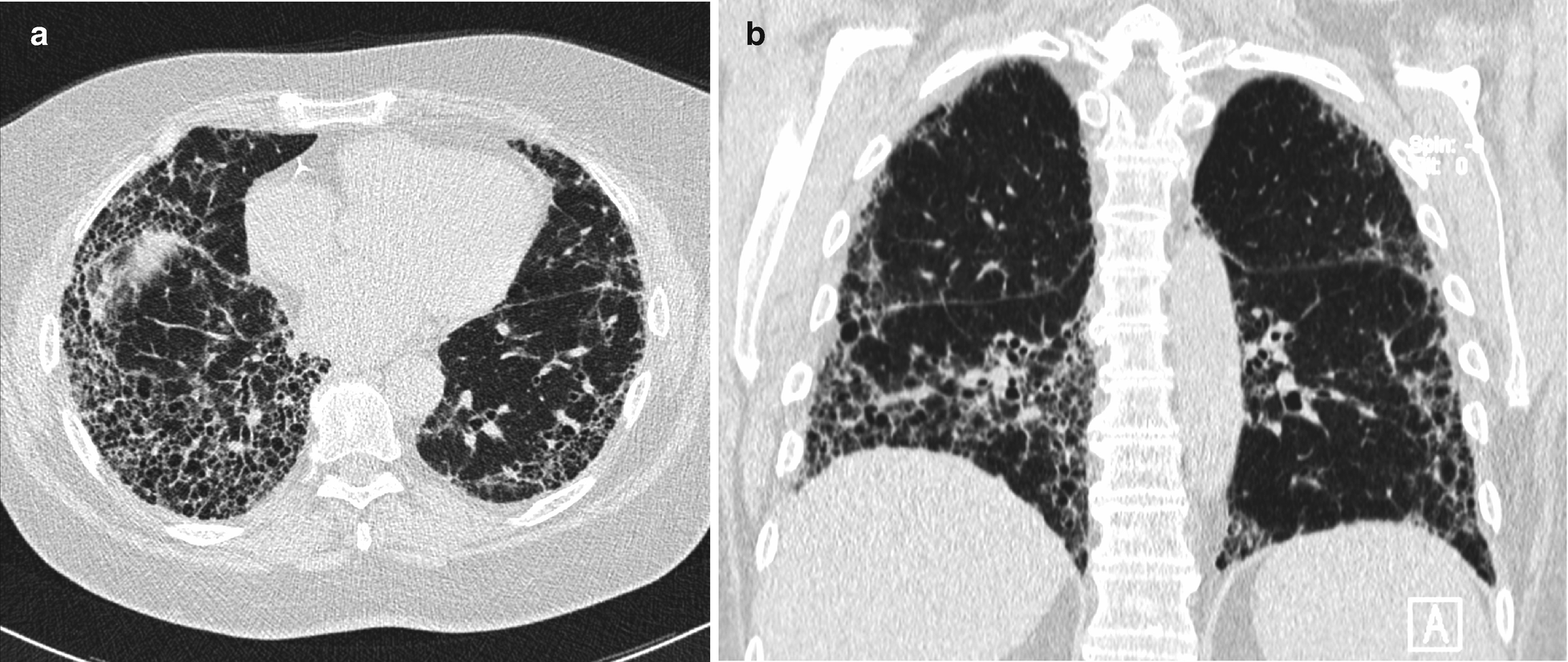
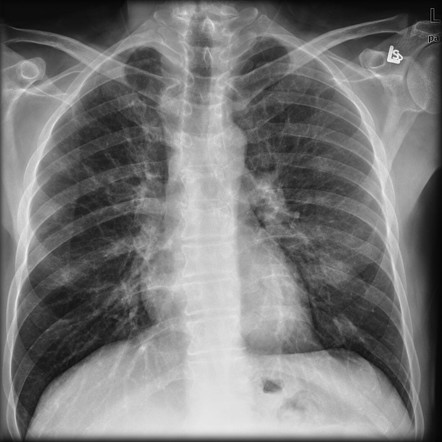
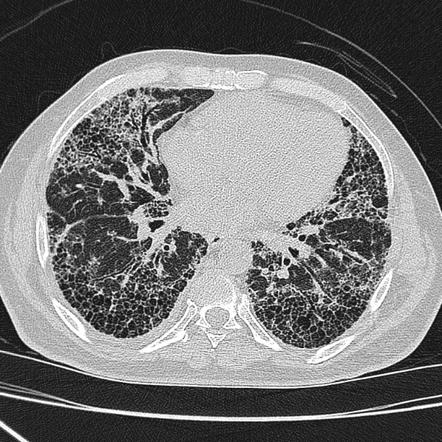
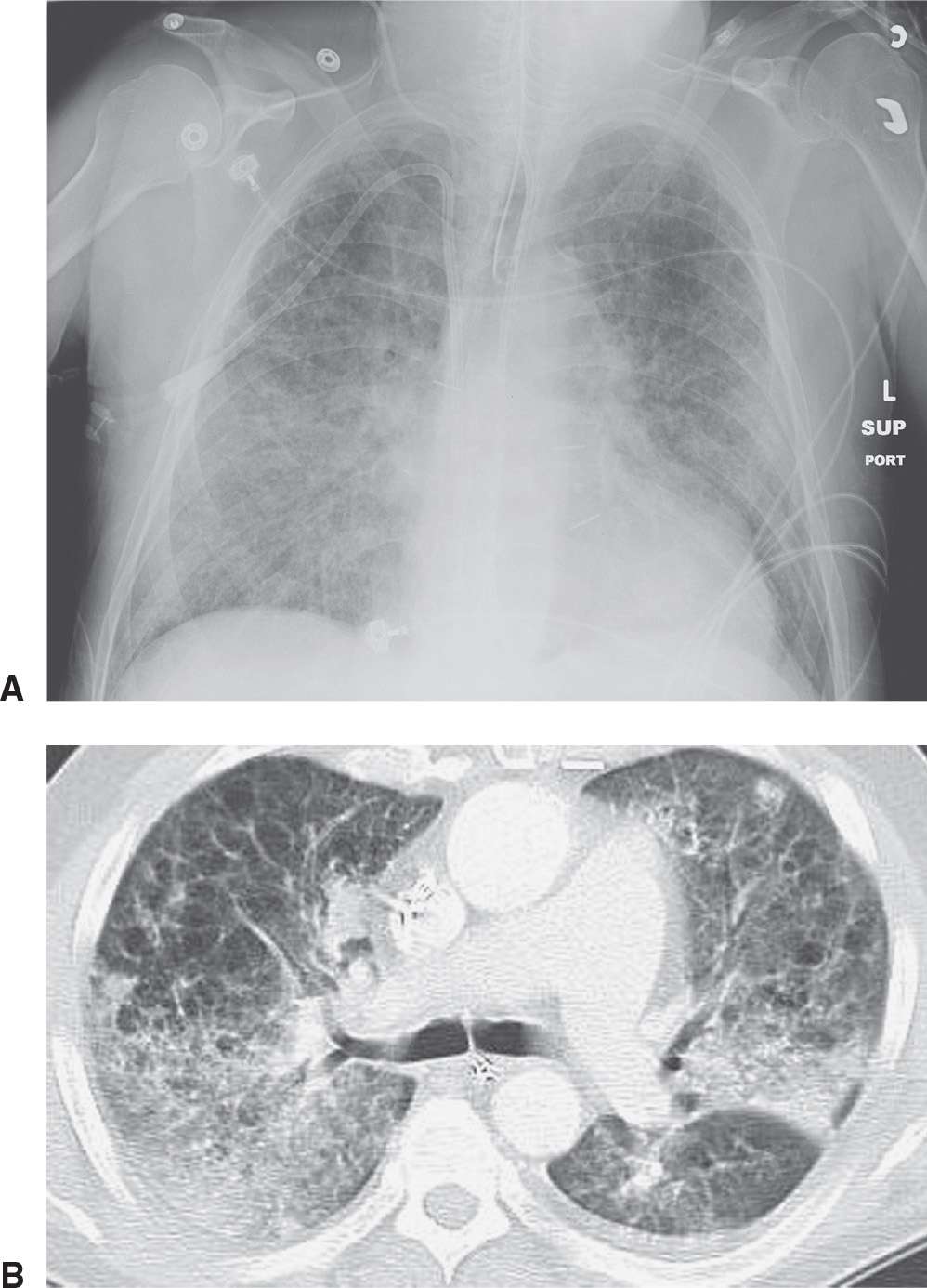
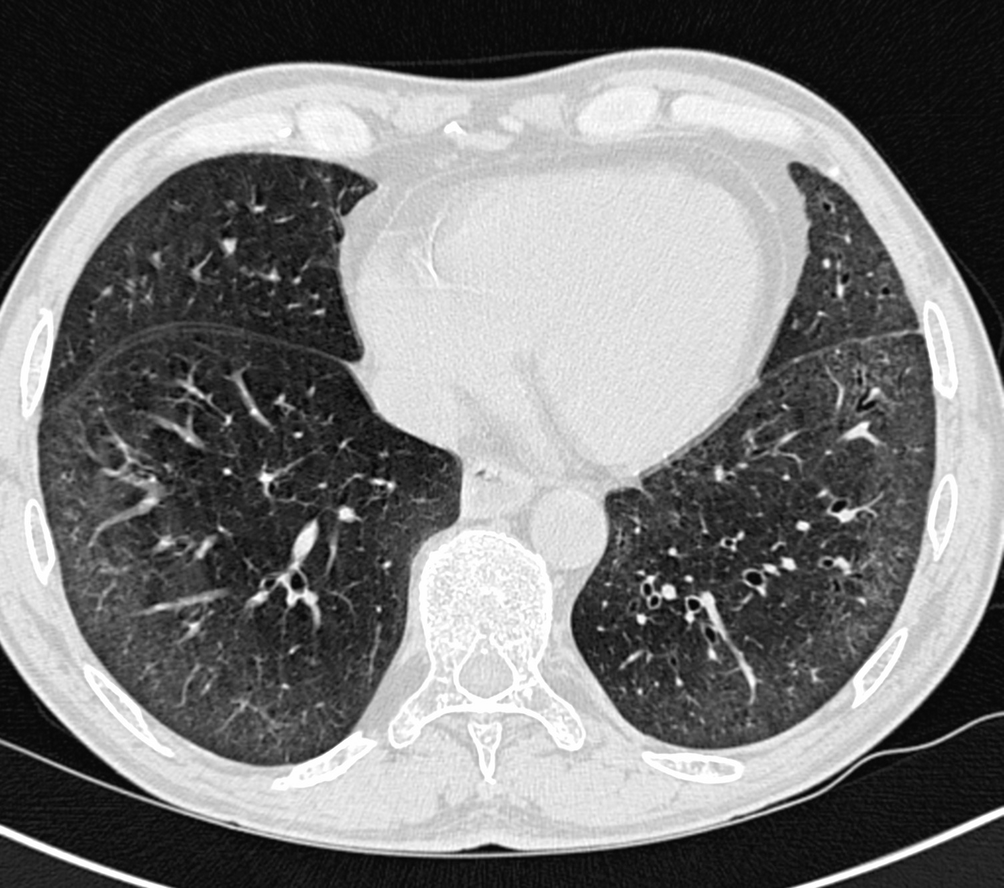
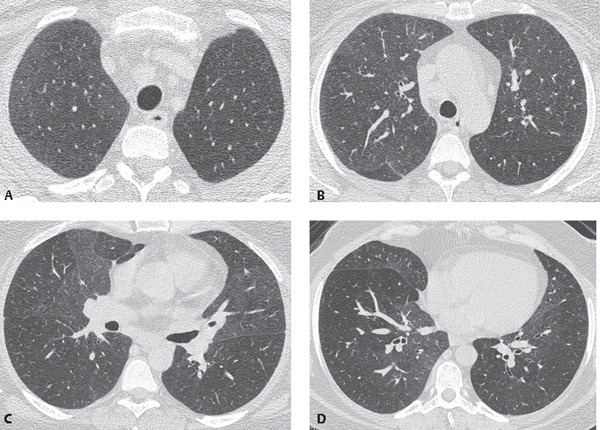
It has a fatal outcome in many cases. Most of our knowledge about imaging findings in interstitial lung disease comes from HRCT. Although rare childhood ILD chILD is associated with significant morbidity and mortality most notably in conditions.
Interstitial lung disease results in six distinct radiologic patterns of abnormality. Interstitial lung disease ILD drug-induced interstitial lung disease. We describe demographic radiologic histopathologic and molecular features and p16 expression in patients with telomeres 10th percentile shortened telomeres and compare them to patients with telomere length 10th percentile.
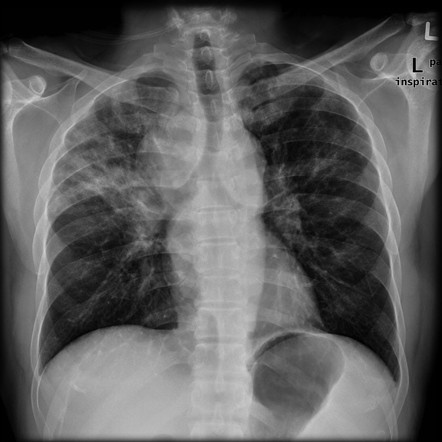
Morphologic classifications of lung conditions diffuse interstitial lung diseases in particular have been undertaken both at the microscopic pathologic patterns and gross radiographic or thin-section computed tomographic CT patterns level. Reticular nodular high and low attenuation table. The lung interstitium is the space where the air sacs called alveoli come in contact with connective tissue and blood vessels to exchange oxygen and carbon dioxide.
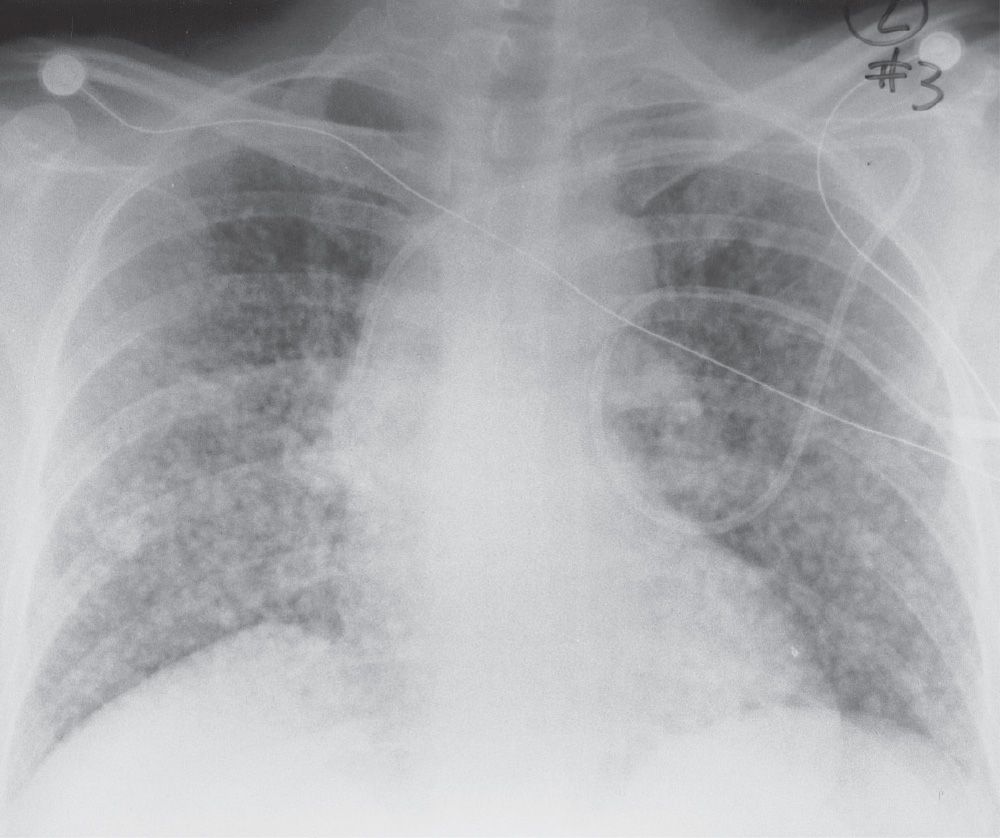
Radiographic evidence of interstitial fibrosis consisting of a reticular pattern that involves mainly the lower lung zones is seen in only about 3 of patients who have systemic lupus erythematosus. Interstitial lung disease ILD in pediatric patients is different from that in adults with a vast array of pathologic conditions unique to childhood varied modes of presentation and a different range of radiologic appearances. By contrast interstitial abnormalities are seen in approximately 30 of patients at high-resolution CT 21 22.
In ILDs scarring damages tissues in or around the lungs air sacs and airways. On HRCT there are four patterns.
IIPs include seven entities.
Lymphoid interstitial pneumonia LIP. Interstitial lung disease ILD drug-induced interstitial lung disease. Introduction Interstitial lung diseases ILDsrepresent a large number of conditions that involve the parenchyma of lung- the alveoli the alveolar epithelium the capillary endothelium and the spaces between these structures as well as perivascular and lymphatic tissues. On HRCT there are four patterns. Although rare childhood ILD chILD is associated with significant morbidity and mortality most notably in conditions. IIPs include seven entities. Nonspecific interstitial pneumonia NSIP. Interstitial lung disease results in six distinct radiologic patterns of abnormality. Lymphoid interstitial pneumonia LIP.
Lymphoid interstitial pneumonia LIP. IIPs include seven entities. Most of our knowledge about imaging findings in interstitial lung disease comes from HRCT. Radiographic evidence of interstitial fibrosis consisting of a reticular pattern that involves mainly the lower lung zones is seen in only about 3 of patients who have systemic lupus erythematosus. The histologic pattern aswell as the HRCT findings in AIP are indistinguishable from acute respiratory distress syndrome ARDS. Diseases that radiographically appear to involve the terminal airspaces or alveoli and those that appear to involve the interstitium. Although rare childhood ILD chILD is associated with significant morbidity and mortality most notably in conditions.
































Post a Comment for "Interstitial Lung Disease Radiology"